[코딩테스트] 그래프의 탐색
reference : 2021 코딩테스트 기초(최백준) 강의를 공부하며 정리한 내용입니다.
그래프의 탐색
- 목적? 한 정점에서 시작해서 연결된 모든 정점을 한 번씩 방문하는 것
- DFS와 BFS는 순서만 다르고 목적은 동일
- DFS : 깊이 우선 탐색
- 사람 1명 시작점, 간선을 통해 그래프 이동. 돌아가야 할 때 스택을 이용
- BFS : 너비 우선 탐색
- 사람 1명 시작점, 갈 수 있는 곳을 사람을 복제해서 이동
깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS)
- 스택을 이용해서 갈 수 있는 만큼 최대한 많이 감. 갈 수 없으면 이전 정점으로 돌아간다.
- check[i] = i를 방문 1(true), 0(false)
- 스택은 재귀로 호출. 함수 호출하면 내부적으로 스택에 들어가서!
- 인접 행렬을 이용한 구현
void dfs(int x){
check[x] = true; //x를 방문함
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
if(a[x][i] == 1 && check[i] == false){
//x,i사이에 간선이 존재 && i를 방문한 적이 없음
dfs(i);
}
}
}
- 각 정점마다 dfs 1번씩 호출 x dfs함수의 복잡도 = V x V = O(V²)
- 인접 리스트를 이용한 구현
void dfs(int x){
check[x] = true;
for(int i=0; i<a[x].size(); i++){
//a[x] = x와 연결된 모든 정점(간선)
int y = a[x][i];
if(check[y] == false){
dfs(y);
}
}
}
- E는 전체 간선의 개수기 때문에 시간복잡도 O(VE)아님! 반복문은 x와 연결되어 있는 간선의 개수만큼만 돌아가서! 즉 모든 정점을 한번씩 방문하니 V, 모든 간선도 한번씩 검사하니 E, O(V+E)
- 대부분의 그래프는 V < E 때문에 O(E) 로 표현해도 됨
너비 우선 탐색 (BFS)
- DFS에서 방문 = 함수의 호출, BFS 방문 = 큐에 넣을때
- 큐를 이용해서 지금 위치에서 갈 수 있는 걸 모두 큐에 넣는 방식
- 큐에 넣을 때 방문했다고 체크해야 함
- 인접행렬, O(V²) 모든 정점 한번씩 방문(큐가 비어있지 않은 동안 반복되니 큐에 한 번씩 push, 한번씩 pop될 때마다 전체 정점 연결 확인하니까)
queue<int> q;
//시작점 1 가정
check[1] = true;
q.push(1);
while(!q.empty()){ //q가 비어있어야 탐색 끝난거니까
int x = q.front(); //가장 앞에있는 앨 x라고 하고
q.pop(); // 빼고
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++){ //이동할 수 있는 모든 i에 대해서
if(a[x][i]==1 && check[i]==false){ //간선 있고, 방문한 적 없으면
check[i] = true; //방문했다
q.push(i); //q에 넣는다
}
}
}
- 인접리스트 O(V+E) -> O(E)
queue<int> q;
check[1] = true;
q.push(1);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0; i<a[x].size(); i++){
//행렬과 다른 건 다음정점 찾는 부분.
int y = a[x][i]; // x가 나오면 x와 연결된 모든 y에 대해서!
if(check[y]==false){ //방문하지 않았으면
check[y] = true; //방문하고
q.push(y); //push
}
}
}
DFS와 BFS (1260번)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260
문제
- 그래프를 DFS로 탐색한 결과와 BFS로 탐색한 결과를 출력하는 문제
풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Integer>[] a;
static boolean[] c;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); //정점
int m = sc.nextInt(); //간선
int start = sc.nextInt(); //시작 정점
a = (ArrayList<Integer>[]) new ArrayList[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
a[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
a[u].add(v);
a[v].add(u);
}
//정렬 이유? 문제에서 정점 여러개면 작은것부터 먼저 방문한다해서
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
Collections.sort(a[i]);
}
c = new boolean[n+1];
dfs(start);
System.out.println();
c = new boolean[n+1];
bfs(start);
System.out.println();
}
private static void dfs(int x) {
if(c[x]) {
return;
}
c[x] = true;
System.out.print(x+" ");
for(int y : a[x]) {
if(c[y]==false) {
dfs(y);
}
}
}
private static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
c[start] = true;
q.add(start);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.remove();
System.out.print(x + " ");
for(int y : a[x]) {
if(c[y]==false) {
c[y] = true;
q.add(y);
}
}
}
}
}
-> 아직 안 익숙해서 코드 많이 참고했다..ㅠㅠ 저렇게 짜는 방법부터 익숙해저야 할듯…
연결요소 (11724번)

- 위 그래프를 두개로 볼 수도, 한 개로 볼 수도 있음.
- 1개라고 볼 땐 나누어진 각각의 그래프를 연결요소라고 함. 즉, 위 그림은 연결요소 총 2개
- 연결 요소에 속한 모든 정점을 연결하는 경로가 있어야 한다. 또, 다른 연결 요소에 속한 정점과 연결하는 경로가 있으면 안된다.
- 연결요소를 구하는 건 DFS나 BFS 탐색을 이용해서 구할 수 있다.
- DFS, BFS가 한 정점에서 연결된 모든 정점을 방문하는 알고리즘이기 때문
- DFS 시작 의미하는 건 연결요소 찾았다는 것.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11724
문제
- 연결요소 구하는 문제
풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Integer>[] a;
static boolean[] c;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); //정점
int m = sc.nextInt(); //간선
a = (ArrayList<Integer>[]) new ArrayList[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
a[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int u=sc.nextInt();
int v=sc.nextInt();
a[u].add(v);
a[v].add(u);
}
c = new boolean[n+1];
int ans = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(c[i]==false) {
dfs(a, c, i);
ans+=1;
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
private static void dfs(ArrayList<Integer>[] a, boolean[] c, int i) {
if(c[i]) {
return;
}
c[i] = true;
for(int y:a[i]) {
if(c[y]==false) {
dfs(a,c,y);
}
}
}
}
이분 그래프 (1707번)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1707
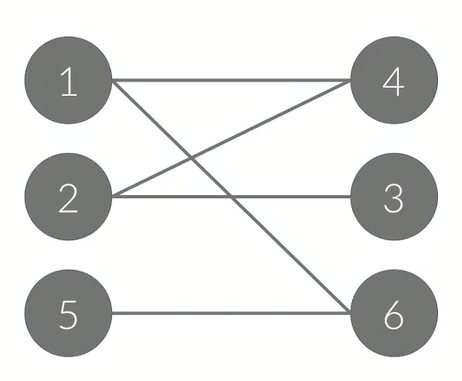
- A에 포함되어 있는 정점끼리 연결된 간선 없음
- B에 포함되어 있는 정점끼리 연결된 간선 없음
- 즉 모든 정점을 A, B로 나눌 수 있어야 함 (125 / 436)
- 모든 간선의 한 끝 점은 A에, 다른 끝 점은 B에
- 위 처럼 A, B 로 나눌 수 있으면 이분 그래프
문제
- 그래프가 이분 그래프인지 아닌지 판별하는 프로그램을 작성
풀이
- 그래프를 DFS 또는 BFS 탐색으로 이분 그래프인지 아닌지 알아낼 수 있음
- color : A, B 둘 중 하나로 칠한다는 의미. 원래 check 로 사용하던 배열
- 0: 방문안함 , 1: A , 2: B
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
for(int k=0; k<t; k++) {
int n = sc.nextInt(); //정점
int m = sc.nextInt(); //간선
ArrayList<Integer>[] a = (ArrayList<Integer>[]) new ArrayList[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
a[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int u=sc.nextInt();
int v=sc.nextInt();
a[u].add(v);
a[v].add(u);
}
int[] color = new int[n+1];
boolean ans = true;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(color[i]==0) {
if(dfs(a, color, i, 1) == false) {
//모든 곳에서 검사해서 하나라도 false나오면 이분그래프 아니다
ans = false;
}
}
}
if(ans) {
System.out.println("YES");
} else {
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
}
private static boolean dfs(ArrayList<Integer>[] a, int[] color, int x, int c) {
color[x] = c;
for(int y:a[x]) {
if(color[y]==0) {
if(dfs(a,color,y,3-c)==false) {
//다음 노드에서 시작했는데 이분그래프가 아니었다면 탐색종료
return false;
}
} else if(color[y]==color[x]) {
//이미 방문했을때 원래 방문 안하는데 색비교를 위해
//둘 컬러가 같을때(a==b)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
단지번호붙이기 (2667번)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2667
문제
- 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다
- 0은 집이 없는 곳, 1은 집이 있는 곳
- 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려고 함
- 연결 : 좌우 아래위로 집이있는 경우
풀이
- 단지 : 연결요소, 단지 크기 : 연결요소에 포함된 정점 개수
- 어떤 곳의 위치를 알고있고, 인접 칸은 네칸밖에 없고 좌표 차로 구할 수 있기 때문에 인접리스트로 구할 필요 x
- 정점 : 정수 2개의 조합, 큐에도 두개 넣어야 한다.
- d[i][j] = (i,j)를 방문 안했으면 0, 했으면 단지 번호
import java.util.*;
class Pair {
int x;
int y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class Main {
static int[][] a;
static int[][] check;
static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 }; // (x-1,y) (x+1,y), (x,y-1), (x,y+1)
static int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
a = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String s = sc.next();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
a[i][j] = s.charAt(j)-'0';
}
}
check = new int[n][n];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (a[i][j] == 1 && check[i][j] == 0) {
bfs(i, j, ++cnt, n);
}
}
}
int[] ans = new int[cnt];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (check[i][j] != 0) {
ans[check[i][j] - 1] += 1;
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(ans);
System.out.println(cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
System.out.println(ans[i]);
}
}
private static void bfs(int x, int y, int cnt, int n) {
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
q.add(new Pair(x,y));
check[x][y] = cnt;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.remove();
x = p.x;
y = p.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 인접한 4개
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < n) { // 범위 안에 있는지 체크
if (a[nx][ny] == 1 && check[nx][ny] == 0) { // 집 있고 방문x면
q.add(new Pair(nx,ny));
check[nx][ny] = cnt;
}
}
}
}
}
}
-> 그래프 연결요소 찾는 문제인건 알겠는데 코드짜는게 어렵다..ㅠ 이게 기본문제라니이이이ㅠㅠㅠ 밑에 문제랑 비교했을 때 여긴 bfs함수 호출 자체를 for문 안에서 돌리고 있는데 그건 아마 연결요소 찾는 거라 그런거겠지..?
//dfs 코드
private static void dfs(int x, int y, int cnt, int n) {
check[x][y]=cnt;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < n) {
if (a[nx][ny] == 1 && check[nx][ny] == 0) {
dfs(nx,ny,cnt,n);
}
}
}
}
미로탐색 (2178번)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2178
문제
- (1,1)에서 (N,M)으로 가는 가장 빠른 길을 구하는 문제
풀이
- 최단 경로기에 DFS 탐색으론 풀 수 없다. (어떻게 이동할지 알 수 없음)
- 최단 경로는 BFS 탐색 사용(단계별로 진행된다는 사실 이용), 가중치 1일때만 가능
import java.util.*;
class Pair {
int x;
int y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class Main {
static int[][] a;
static int[][] d;
static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 }; // (x-1,y) (x+1,y), (x,y-1), (x,y+1)
static int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
a = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String s = sc.next();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
a[i][j] = s.charAt(j)-'0';
}
}
d = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
d[i][j] = -1;
}
}
bfs(0,0,n,m);
System.out.println(d[n-1][m-1]);
}
private static void bfs(int x, int y, int n, int m) {
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
q.add(new Pair(x,y));
d[x][y] = 1;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.remove();
x = p.x;
y = p.y;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = x+dx[i];
int ny = y+dy[i];
if(0<=nx && nx<n && 0<=ny && ny<m) {
if(a[nx][ny]==1 && d[nx][ny]==-1) {
q.add(new Pair(nx,ny));
d[nx][ny] = d[x][y]+1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
토마토 (7576번)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
문제
- 하루가 지나면, 익은 토마토의 인접한 곳에 있는 익지 않은 토마토들이 익게 된다.
- 인접한 곳 : 앞, 뒤, 왼쪽, 오른쪽
- 토마토가 저절로 익는 경우는 없다.
- 상자안의 익은 토마토와 익지 않은 토마토가 주어졌을 때, 며칠이 지나면 토마토가 모두 익는지 구하라
풀이
- 미로탐색과 매우 비슷한 문제
import java.util.*;
class Pair {
int x;
int y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class Main {
static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 }; // (x-1,y) (x+1,y), (x,y-1), (x,y+1)
static int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] a = new int[n][m];
int[][] d = new int[n][m];
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
a[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
d[i][j] = -1;
if (a[i][j] == 1) {
q.add(new Pair(i, j));
d[i][j] = 0; //저장될때부터 익어있는 상태면 0출력이니까
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.remove();
int x = p.x;
int y = p.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < m) {
if (d[nx][ny] == -1 && a[nx][ny] == 0) {
q.add(new Pair(nx, ny));
d[nx][ny] = d[x][y] + 1;
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
if(ans < d[i][j]) {
ans = d[i][j];
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
if(a[i][j]==0 && d[i][j]==-1) {
ans = -1;
}
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
-> 가로 m, 세로 n인데 배열을 a[n][m]으로 설정해도 어차피 나오는 값은 같아서 상관 없나보다…?
나이트의 이동 (7562번)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7562
문제
- 체스판 위에 한 나이트가 있을 때, 나이트가 이동하려고 하는 칸이 주어짐
- 이 때, 최소 몇 번만에 이동할 수 있는지 구하는 문제
풀이
- 미로탐색과 매우 비슷한 문제
- 차이점은 딱 하나. 나이트 이동 범위가 다름. dx, dy 설정 다르게…
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dx = { -2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
static int[] dy = { 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-->0) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
int sx = sc.nextInt();
int sy = sc.nextInt();
int ex = sc.nextInt();
int ey = sc.nextInt();
int[][] a = new int[n][n];
int[][] d = new int[n][n];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(d[i], -1); //이런 편리한 메소드가 있었다니
}
q.add(sx); q.add(sy);
d[sx][sy] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.remove();
int y = q.remove();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < n) {
if (d[nx][ny] == -1) {
q.add(nx);
q.add(ny);
d[nx][ny] = d[x][y] + 1;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(d[ex][ey]);
}
}
}
-> 여전히 한번에 맞추지 못하지만^^… 코드에 조금씩 익숙해져 가는 중.. 이 문제는 전체 상태가 나오는게 아니니까 굳이 Pair를 만들 필요가 없는듯
댓글남기기